Choosing the right stamped sheet metal for your project is crucial for ensuring its success and longevity. With numerous options available, determining which material best meets your specific needs can be overwhelming. As industry expert John Smith, a leading engineer in the stamped sheet metal sector, advises, "Selecting the correct stamped sheet metal is not just about finding the right thickness; it’s about understanding the unique requirements of your project and how the metal will perform under various conditions."
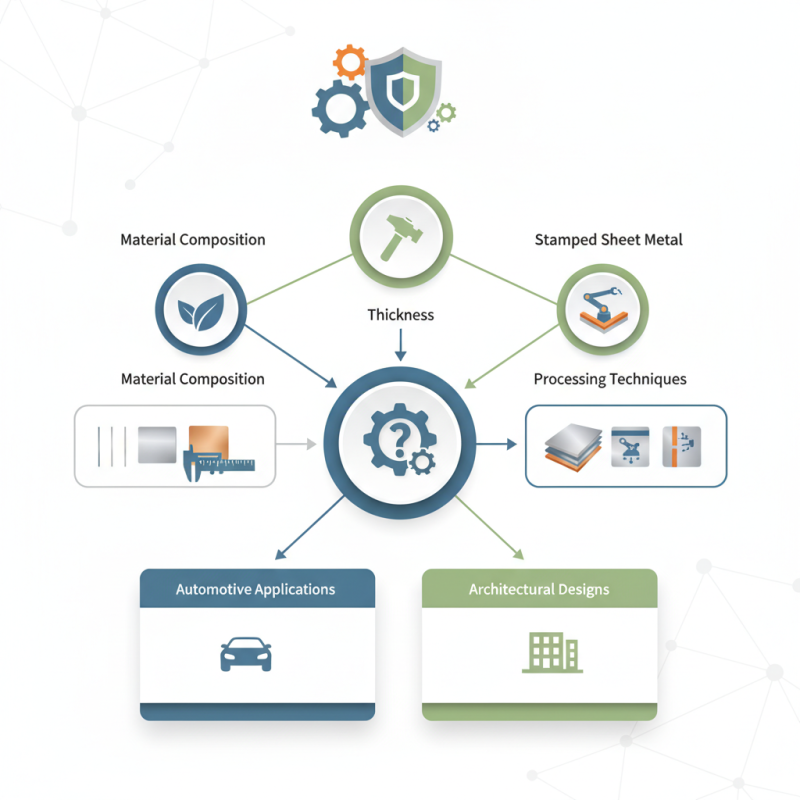
In this guide, we will explore the key factors to consider when selecting stamped sheet metal, from material composition to thickness and processing techniques. By understanding these elements, you can make an informed choice that enhances your project’s functionality and durability. From automotive applications to architectural designs, stamped sheet metal plays a pivotal role in many industries, and knowing how to select the appropriate type is essential for achieving optimal results.

Stamped sheet metal is a versatile material used in a wide range of applications due to its unique properties and manufacturing process. This material is created through a stamping process where sheets of metal are shaped and transformed into specific geometries using dies. The resulting products can vary greatly in complexity, from simple brackets to intricate components found in automotive and aerospace industries. The ability to produce parts with precision and repeatability makes stamped sheet metal an essential choice for manufacturers looking to ensure high quality and consistency in their projects.
Understanding the applications of stamped sheet metal is crucial when selecting the right material for your needs. It is commonly used in industries such as construction, electronics, and consumer goods, where strength, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness are critical. Depending on the specific requirements of a project, different types of sheet metal—such as aluminum, stainless steel, or galvanized steel—may be chosen for their distinct characteristics. For instance, aluminum offers excellent corrosion resistance and is favored in applications where weight is a concern, while stainless steel is often selected for its added strength and durability. By carefully considering the material properties and the specific requirements of your project, you can effectively determine the most suitable stamped sheet metal for your application.
When selecting stamped sheet metal for your project, several key factors come into play that can significantly influence the overall effectiveness and feasibility of your design. First and foremost, consider the material type that best suits your application. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and stainless steel, each offering distinct properties such as weight, corrosion resistance, and cost. For instance, aluminum is lightweight and resistant to oxidation, making it an excellent choice for applications where weight savings are paramount. Conversely, if strength and durability are required, carbon steel may be more appropriate despite its heavier weight.
Another crucial factor is the thickness of the sheet metal. The thickness not only affects the strength and rigidity of the final product but also impacts the complexity of the stamping process. Thicker sheets may require more robust tooling and can be more challenging to work with in terms of bending and shaping. Additionally, evaluating the required tolerances and finishes is important; different projects may demand varying levels of precision and surface aesthetics. Finally, budget constraints should not be overlooked, as material type and thickness can significantly influence overall costs. Balancing these factors with your project's specific requirements will ensure that you make an informed choice in selecting the right stamped sheet metal.
| Factor | Description | Importance Level |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Different materials such as aluminum, steel, and copper offer various strengths and properties. | High |
| Thickness | The thickness of the sheet metal affects durability, weight, and flexibility. | Medium |
| Finish | Surface finishes can enhance aesthetics and corrosion resistance. | Medium |
| Cost | Pricing can vary based on material, thickness, and finishes. | High |
| Application | Consider the intended use - structural vs. decorative. | High |
| Customizability | Ability to meet specific design and manufacturing requirements. | Medium |
When selecting stamped sheet metal for your project, understanding the types of materials available is crucial. The most common materials used in stamped sheet metal include aluminum, steel, stainless steel, and copper. According to industry reports, aluminum is favored for its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal choice for applications in the automotive and aerospace sectors. Research indicates that the aluminum sheet market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5% over the next five years, driven by increasing demand for lightweight materials.
Steel, particularly carbon steel, remains an industry staple due to its high strength and affordability. A 2022 statistical overview highlighted that over 70% of stamped metal components are made from various steel alloys, reflecting its widespread acceptance in manufacturing. Stainless steel, known for its excellent corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, is often used in products requiring hygiene, such as kitchen equipment and medical devices. Recent analyses show that the demand for stainless steel is expected to rise, particularly in the construction and food processing industries. Meanwhile, copper is appreciated for its electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for stamped components in the electronics sector.
By understanding these materials and their properties, project managers can make informed decisions that optimize performance and cost-effectiveness. Each type of metal offers distinct advantages that must be carefully matched to the specific requirements of the project, whether it involves structural integrity, weight considerations, or resistance to environmental factors.
When selecting stamped sheet metal for a project, determining the appropriate thickness is crucial to ensure optimal performance and durability. According to industry standards, sheet metal thickness is often measured in gauge, where a lower gauge number indicates a thicker material.
For instance, materials with a thickness of 0.25 inches (approximately 6.35 mm) or more are generally considered suitable for heavy-load applications, such as structural support or heavy machinery housing, as they provide better strength and resistance to deformation.
To effectively choose the right thickness, one must consider the specific requirements of the project, including load-bearing capabilities, environmental factors, and fabrication processes. The Engineering Toolbox indicates that for most applications, a thickness range of 0.030 to 0.125 inches (0.76 to 3.18 mm) is typical. Thinner sheets may work for non-load-bearing components, while thicker sheets are imperative for parts that undergo significant stress or require heightened resilience against potential impacts.
Furthermore, considerations such as corrosion resistance should also influence thickness choice; for example, projects exposed to harsh weather conditions may benefit from thicker materials that better withstand the elements.
In summary, the selection of the right sheet metal thickness not only impacts the overall functionality of the project but can also determine the long-term reliability of the finished product. Adhering to established guidelines and tailoring choices to specific project demands can optimize performance and extend the life of stamped sheet metal components.
Stamped sheet metal is a versatile solution widely used across various industries. The automotive sector, for example, relies heavily on stamped sheet metal components for vehicle frames, body panels, and many interior parts. The precision and ability to create complex shapes with minimal waste make it an essential material for manufacturers aiming for efficiency and quality in vehicle production.
Another industry that significantly benefits from stamped sheet metal is construction. Professionals utilize it for structural components, roofing, and siding, providing durability and strength while maintaining aesthetic appeal. The ability to customize sheet metal to fit specific architectural designs means that it caters effectively to both functional requirements and design innovations in building projects.
In the electronics sector, stamped sheet metal finds applications in enclosures, heat sinks, and mounts. This is crucial for ensuring that electronic devices are both protected and effectively dissipate heat. The efficiency in production that stamped metal offers allows for scalable solutions in a field that constantly demands innovation and adaptability. Thus, the versatility of stamped sheet metal continues to make it a cornerstone across these diverse industries.
This bar chart illustrates the percentage of usage of stamped sheet metal across various common industries, highlighting the automotive sector as the leading user, followed by construction and electronics.